# Initialize Otter
import otter
grader = otter.Notebook("Homework_1_Hello_World_Python.ipynb")
Homework 1 - Hello World in Python#
Python is a simple - compared to others - programming language. It is a good language to start with. In this homework, you will learn how to write a simple program in Python. The goal of this homework is to get you familiar with the programming environment and the tools we will use in this course. You will also learn how to do basic operations in Python.
Note
We realize that generative AI tools like ChatGPT are highly capable of solving all problems in this class. ChatGPT is a helpful tool to facilitate learning new approaches and coding concepts. However, ChatGPT has its limits, and the more you learn, the better your prompts will be. This will allow you to solve more complex problems faster. In this course we are expecting you to have a detailed understanding of the concepts covered in the homework. This will be tested in the quizzes and exams, where ChatGPT will not be available. Past experience has shown that students who rely on ChatGPT for homeworks and do not learn the concepts, struggle in the quizzes and exams.
Starting Your Assignment#
Navigate to the assignment on the course website. Click on the rocket icon to launch the assignment in the JupyterHub.
Part 1: Entering Your Information for Credit#
To receive credit for assignments it is important we can identify your work from others. To do this we will ask you to enter your information in the following code block.
Before you begin#
Run the block of code at the top of the notebook that imports and sets up the autograder. This will allow you to check your work.
# Please provide your first name, last name, Drexel ID, and Drexel email. Make sure these are provided as strings. "STRINGS ARE TEXT ENCLOSED IN QUOTATION MARKS."
# In the assignments you will see sections of code that you need to fill in that are marked with ... (three dots). Replace the ... with your code.
first_name = ...
last_name = ...
drexel_id = ...
drexel_email = ...
grader.check("q0-Checking-Your-Name")
from friendly.jupyter import *
Question 1: Importing Packages and Doing Math#
The power of python comes from the packages that are available for it. In this question, you will learn how to import packages and use them to do math.
Write a Python code to import the math package and then use it to calculate the square root of 256. Print the result.
Example 1#
To help you we provide an example for you to understand the syntax required. All homework assignments will be wrapped in a function for grading purposes. For now, just ignore the def function_name(): and return lines. We will explain them later in teh course. For now just focus on the code inside the function.
Question:#
Write a Python code to import the math package and then use it to calculate the natural logarithm of 20. print the result.
# Import the math package
import math
def example_1():
# Calculate and print the natural logarithm of 20
log_20 = math.log(20)
output = print(log_20)
return output
# import required packages here
...
# This line of code defines a function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
def question_1(printing=True):
# Calculate the square root of 256
# Python is sensitive to indentation, so make your code is indented as provided
sqrt_256 = ...
# This is an if statement that controls if the output is printed
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
if printing:
# print the output of the result
output = ...
# This line of code returns variables
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
return sqrt_256
# This line of code calls the function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
sqrt_256 = question_1()
grader.check("q1-Conducting-Simple-Math")
Question 2: Applying Simple Mathematical Operations#
Write a Python program that calculates and prints the result of the following operations:
The sum of a=15 and b=23.
The product of c=12 and d=4.
The division of e=48 by f=6.
The remainder when g=17 is divided by h=5.
# This line of code defines a function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
def question_2():
a = ...
b = ...
c = ...
d = ...
e = ...
f = ...
g = ...
h = ...
sum_result = ...
product_result = ...
division_result = ...
remainder_result = ...
# This line of code returns variables
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
return (sum_result, product_result, division_result, remainder_result, a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h)
# This line of code calls the function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS CODE
output = question_2()
# Print the results
print("Sum result:", output[0])
print("Product result:", output[1])
print("Division result:", output[2])
print("Remainder result:", output[3])
grader.check("q2-Applying-Simple-Mathematical-Operations")
Question 3: Basic Printing of Strings#
Print the following sentence in Python: Hello, Python world! Make sure to include the exclamation mark.
# This line of code defines a function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
def question_3():
string = ...
output = ...
# This line of code returns variables
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
return output, string
# This line of code calls the function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
output = question_3()
grader.check("q3-Basic-Printing-of-Strings")
Question 4: Assigning Variable and Operations on Variables#
Create two variables: a and b. Assign the value 10 to a and the value 20 to b. Then, create a third variable c that stores the sum of a and b. Print the value of c.
# This line of code defines a function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
def question_4(printing=True):
a = ...
b = ...
c = ...
# This is an if statement that controls if the output is printed
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
if printing:
# your print statement
...
return a, b, c
# This line of code calls the function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
a, b, c = question_4()
grader.check("q4-Assigning-Variable-and-Operations-on-Variables")
Question 5: Printing Text with Variables#
Create a variable named course and assign it the value “Drexel ENGR131”. Then, print the following sentence using this variable: “I am currently taking [course].”
# This line of code defines a function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
def question_5(*args, printing=True):
...
# This line of code allows us to modify your variable so we can test you did not hard code the problem
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS CODE
if args:
course += args[0]
# This is an if statement that controls if the output is printed
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
if printing:
# your print statement, make sure it is at this indentation level
...
# This line of code returns variables
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
return course
# This line of code calls the function
# DO NOT CHANGE THIS LINE OF CODE
output = question_5()
grader.check("q5-Printing-Text-with-Variables")
Submitting Your Assignment#
To submit your assignment please use the following link the assignment on GitHub classroom.
Use this link to navigate to the assignment on GitHub classroom.
If you need further instructions on submitting your assignment please look at Lab 1.
Viewing your score#
Each .ipynb file you have uploaded will have a file with the name of your file + Grade_Report.md. You can view this file by clicking on the file name. This will show you the results of the autograder.
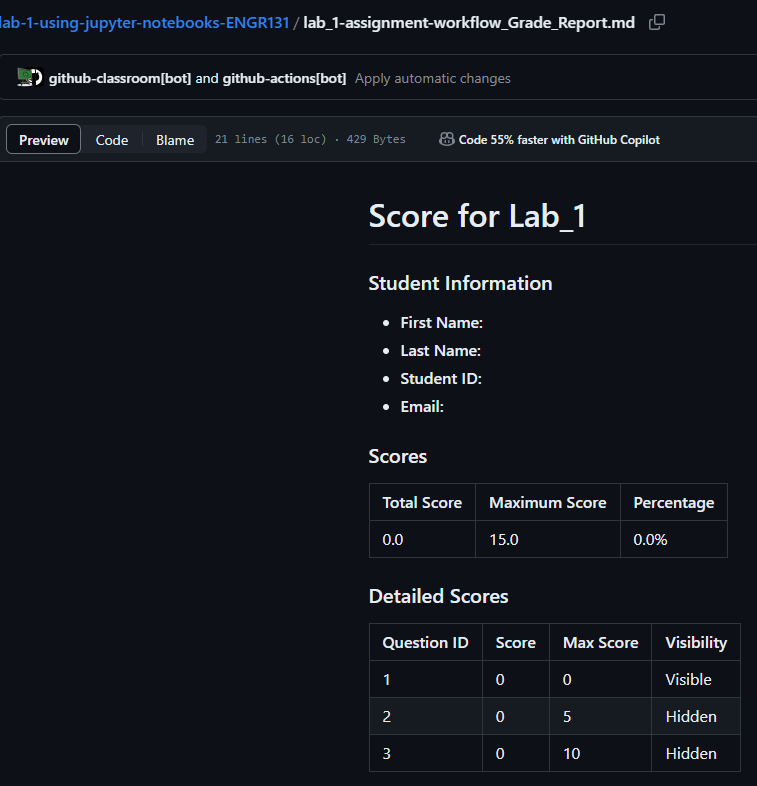
We have both public and hidden tests. You will be able to see the score of both tests, but not the specific details of why the test passed or failed.
Note
In python and particularly jupyter notebooks it is common that during testing you run cells in a different order, or run cells and modify them. This can cause there to be local variables needed for your solution that would not be recreated on running your code again from scratch. Your assignment will be graded based on running your code from scratch. This means before you submit your assignment you should restart the kernel and run all cells. You can do this by clicking Kernel and selecting Restart and Run All. If you code does not run as expected after restarting the kernel and running all cells it means you have an error in your code.


