📝 Introduction to Branching
Contents
📝 Introduction to Branching#
Utility of branching#
Branching causes specific blocks of code to be executed only under certain conditions. The conditions are articulated as logical expressions.
How do you write branching statements?#
The simplest version of branching statement is an “if statement”.
if logical_expression:
code_block
More complex structures are possible with “if-else statements”.
if logical_expression_A:
code_block_1
elif logical_expression_B:
code_block_2
elif logical_expression_C:
code_block_3
else:
code_block_4
Using branching in basic control theory#
Many engineering interventions aim to maintain an optimal setting in a system. Control theory is the basis for achieving these optimal conditions as smoothly and consistently as possible.
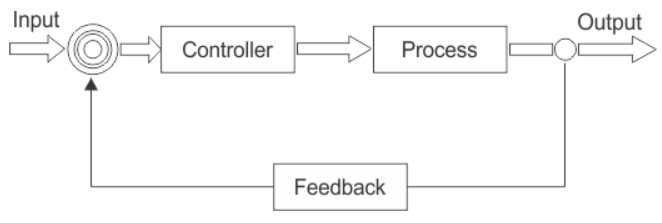
One very common example is temperature control in buildings.
Architectural engineers learn how to design heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems throughout buildings that allow temperature in a room to be controlled.
Electrical engineers help with innovating the sensors and controls that allow for the temperature to be optimized.
Material scientists improve designs of windows and doors to enhance the controllability of the temperature and sustainability of the optimal conditions.
The thermostat typically acts as both the sensor collecting feedback and the controller determining whether the process should be heating, cooling, or no intervention.
The very simplest process control requires only the process variable, or the room temperature in this case, and the set point, or the desired temperature in this case.
def thermostat(roomTemp, desiredTemp):
"""
Changes the status of the thermal control devices based
on the room temperature and desired temperature
(Python Numerical Methods, MIT license)
:type temp: Int
:type desiredTemp: Int
:rtype: String
"""
if roomTemp < desiredTemp - 5:
device = "heat"
elif roomTemp > desiredTemp + 5:
device = "AC"
else:
device = "nothing"
return device
currentT = 58
desiredT = 64
device = thermostat(currentT, desiredT)
print(
f"When the temperature is {currentT} degrees Fahrenheit, activate {device} to achieve {desiredT} degrees Fahrenheit."
)
When the temperature is 58 degrees Fahrenheit, activate heat to achieve 64 degrees Fahrenheit.
currentT = 85
desiredT = 78
device = thermostat(currentT, desiredT)
print(
f"When the temperature is {currentT} degrees Fahrenheit, activate {device} to achieve {desiredT} degrees Fahrenheit."
)
When the temperature is 85 degrees Fahrenheit, activate AC to achieve 78 degrees Fahrenheit.
currentT = 80
desiredT = 75
device = thermostat(currentT, desiredT)
print(
f"When the temperature is {currentT} degrees Fahrenheit, activate {device} to achieve {desiredT} degrees Fahrenheit."
)
When the temperature is 80 degrees Fahrenheit, activate nothing to achieve 75 degrees Fahrenheit.
Perhaps you have a roommate who is very sensitive to temperature changes. How could you change the thermostat function to keep the room temperature closer to the set point?
def thermostat(roomTemp, desiredTemp):
"""
Changes the status of the thermal control devices based
on the room temperature and desired temperature
(Python Numerical Methods, MIT license)
:type temp: Int
:type desiredTemp: Int
:rtype: String
"""
if roomTemp < desiredTemp - 5:
device = "heat"
elif roomTemp > desiredTemp + 5:
device = "AC"
else:
device = "nothing"
return device
What are at least three other processes you can think of that would similarly rely on branching, especially in your field of study?
In these systems, which ones have redundancy (e.g., a second method of accomplishing the same thing) either in the sensor that detects the process variable or the processes that can be used to control the process variable?
The notes for Session 5 benefitted from the availability of Python Programming and Numerical Methods: A Guide for Engineers and Scientists through the MIT License.



