📝 🌐 Internet and Networking Overview#
📌 What is the Internet?#
The Internet is a vast global network that connects billions of devices. It enables communication, information sharing, and commerce worldwide.

Key Facts:#
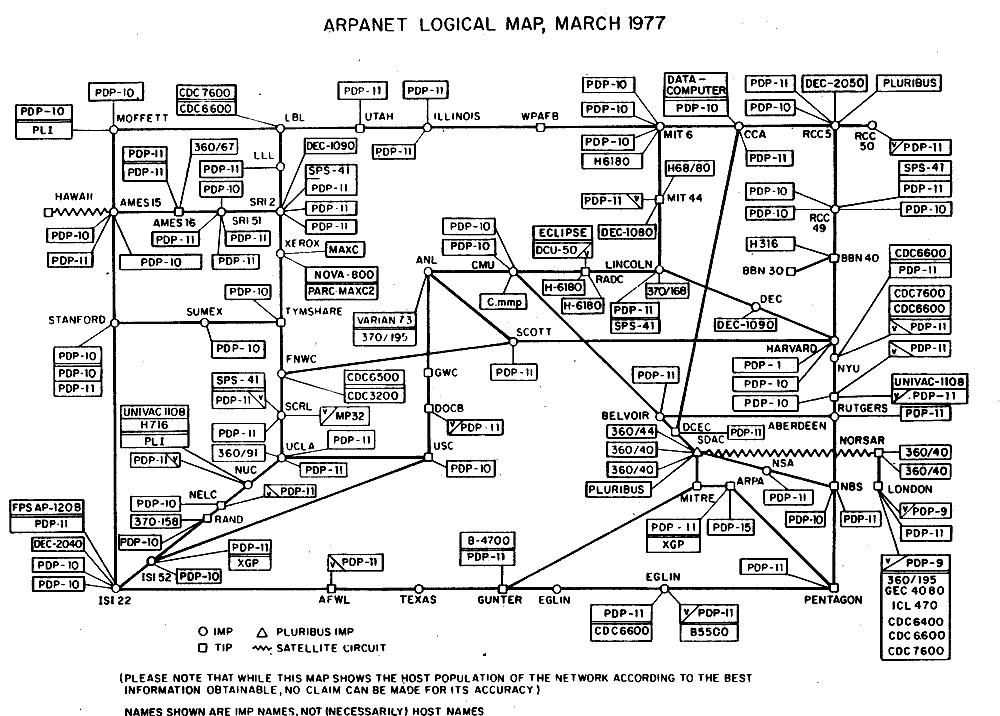
Initially developed as ARPANET in the 1960s by the U.S. Department of Defense.
Currently, there are over 5 billion active users on the Internet.
Operates based on the TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) suite.
Fun Fact: The first message ever sent over the Internet was “LO” (an attempt to send “LOGIN” before the system crashed!).
📡 What is Networking?#
Networking involves connecting devices to facilitate data exchange.

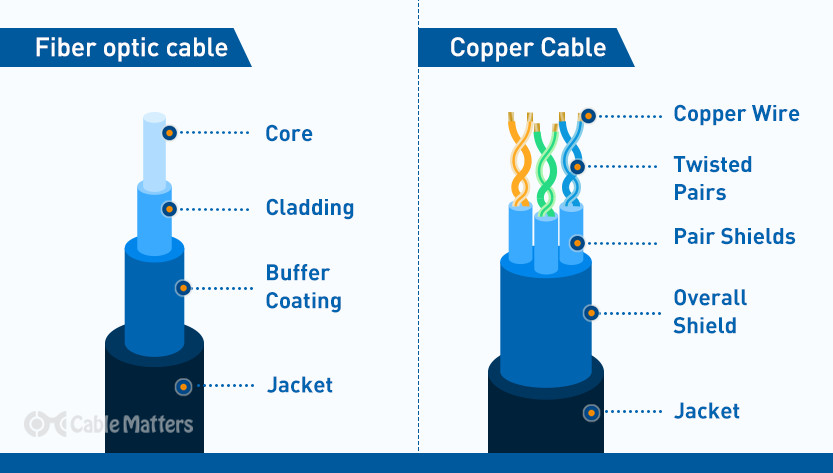
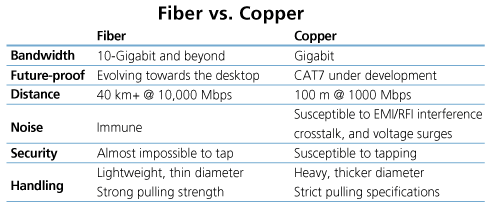
Types of Networks:#
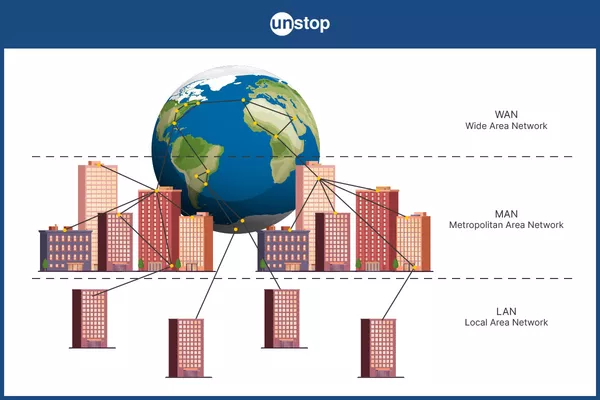
Local Area Network (LAN): Limited to a specific location, such as an office or home.
Wide Area Network (WAN): Covers broader regions (e.g., the Internet).
Wireless Networks: Use radio signals for communication (Wi-Fi, 4G, 5G).
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): Covers a city or a large area.
Personal Area Network (PAN): Connects personal devices like phones and smartwatches.
Fun Fact: “Wi-Fi” doesn’t actually stand for anything; it was just a catchy marketing term!

🔢 Understanding IP Addresses#
Every device on the Internet is assigned a unique IP (Internet Protocol) Address to communicate.
IPv4 vs. IPv6:#
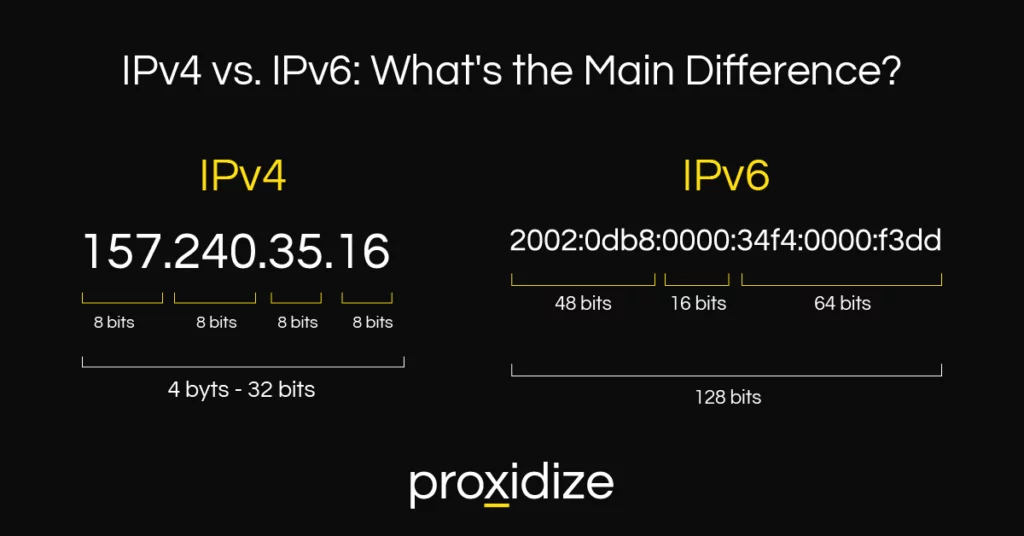
IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4): Uses a 32-bit address format, allowing for 4.3 billion unique addresses (e.g.,
192.168.1.1).IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6): Uses a 128-bit address, allowing for 340 undecillion unique addresses (
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
Public vs. Private IP Addresses#
Public IPs: Assigned by ISPs (Internet Service Providers) and used to identify devices on the Internet.
Private IPs: Used within internal networks (e.g., home or office LANs).
Common private ranges:
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
Fun Fact: IPv6 provides enough IP addresses to assign one to every atom on Earth!
🖥️ How the Internet Works#
When you visit a website (www.example.com):
Your device queries a DNS (Domain Name System) server to get the site’s IP address.
Your browser sends a data request using HTTP/HTTPS.
The request travels through routers, switches, and ISPs.
The web server hosting the website processes the request and sends data back.
Your browser receives and renders the page.
Fun Fact: The first website ever created is still online: http://info.cern.ch!
🌍 Scale of the Internet#
Over 1.5 billion websites exist today.
330 million domain names are registered.
Data transmission speeds reach petabits per second over backbone networks.
Google processes 8.5 billion searches per day!
Fun Fact: The total weight of all the electrons in the Internet’s data is only 50 grams—about the weight of a strawberry!
🛠️ Key Networking Components#
Router#

A router directs traffic between networks and ensures that data packets reach their correct destinations.
It operates at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model.
Can connect multiple networks and manage both wired and wireless connections.
Often assigned a public IP address to act as a gateway to the Internet.
Switch#

A switch connects devices within a LAN (Local Area Network) and forwards data only to the intended recipient.
Operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model.
Can be managed (configurable) or unmanaged (plug-and-play).
Firewall#

A firewall is a security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic.
Can be hardware-based (dedicated devices) or software-based (running on a computer or router).
Uses predefined rules to block or allow network packets.
Helps prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats.
📌 Typical Network Configurations#
Home Network (Basic LAN Setup)#
Router connects to the ISP and assigns IP addresses.
Switch (if needed) connects additional devices like PCs, smart TVs, and printers.
Firewall (built into router) secures the network.
Devices use private IP addresses and access the Internet via NAT (Network Address Translation).
Enterprise Network (Complex Setup)#
Multiple routers for redundancy and load balancing.
Layer 3 switches for efficient internal routing.
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems for security.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) for secure remote access.
Fun Fact: Large enterprises often use multiple firewalls to segment internal networks for security reasons.
🔐 Internet Security#
To stay safe online:
Encryption (HTTPS): Protects data during transmission.
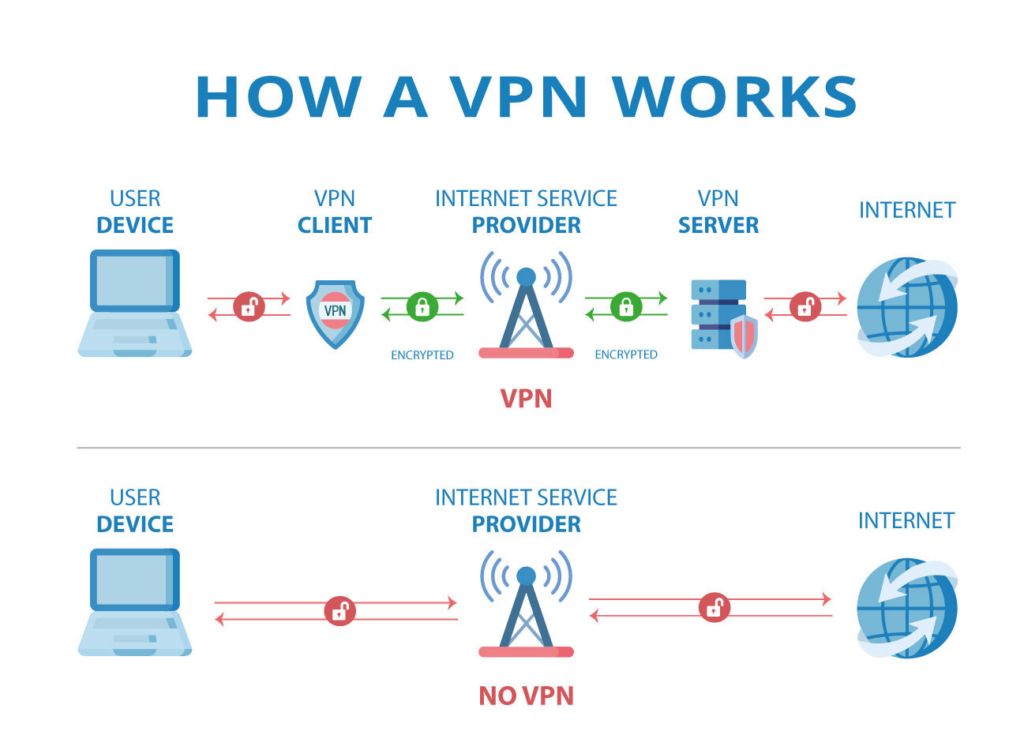
VPN (Virtual Private Network): Masks IP addresses.
Firewalls: Block unauthorized traffic.
2FA (Two-Factor Authentication): Adds an extra security layer.
Fun Fact: The longest password cracked by brute force took 4.5 years!
🚀 Every search, stream, and click travels thousands of miles in milliseconds!

