✨ 🚀 Composable Software Deployments on Kubernetes✨#
🎯 Why Does This Matter?#
In today’s world, software isn’t just installed on a single computer or server—it runs across multiple locations, scales dynamically, and updates continuously. Composable software deployments allow teams to build, deploy, and manage applications that can adapt to change effortlessly.
🌟 Real-World Impact of Composable Deployments#
✅ Online Shopping Platforms – Handle millions of users and update features without downtime.
✅ Streaming Services (e.g., Netflix, YouTube) – Scale dynamically based on user traffic.
✅ AI & Machine Learning Workflows – Process vast amounts of data efficiently.
✅ Banking & Finance – Ensure secure, always-available transactions.
🏗 What is Composable Software Deployment?#
Composable software deployment is the practice of breaking applications into modular, reusable components that can be independently deployed, scaled, and updated. Think of it like LEGO blocks—each block (or service) has a specific role and can be replaced or improved without rebuilding the entire structure.
Why is Composability Important?#
✅ Scalability – Applications can grow as demand increases.
✅ Flexibility – Teams can update and replace parts of an application without affecting the whole system.
✅ Resilience – If one part fails, the entire system doesn’t go down.
✅ Automation – Enables efficient workflows, reducing human error and operational costs.
📦 What is Containerization?#
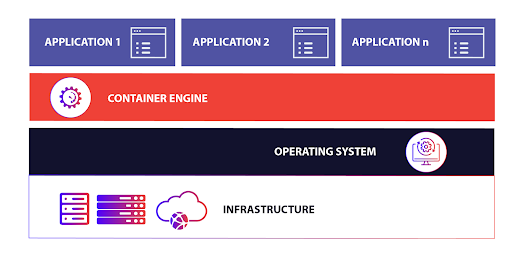
Containerization is a lightweight method for packaging applications along with their dependencies so they can run consistently across different environments.
How Containers Work#
Each container includes the application code, libraries, and dependencies.
Containers run consistently across different machines, avoiding the “works on my machine” problem.
They are isolated from each other, meaning one application’s failure does not affect others.
Why Containers Matter?#
✅ Portability – Runs anywhere, from a laptop to the cloud.
✅ Efficiency – Uses fewer system resources than Virtual Machines (VMs).
✅ Consistency – Eliminates deployment issues by keeping everything self-contained.
✅ Scalability – Easily spins up/down new instances based on demand.
Containers vs. Virtual Machines (VMs)#
Feature |
Containers |
Virtual Machines (VMs) |
|---|---|---|
Size |
Lightweight (~MBs) |
Heavy (~GBs) |
Startup Time |
Seconds |
Minutes |
Resource Efficiency |
Shares OS kernel |
Requires full OS per VM |
Portability |
Runs anywhere |
Limited by OS & hypervisor |
Why Kubernetes and Containers Work Together
Kubernetes orchestrates containers, ensuring they are deployed, scaled, and managed automatically.
Instead of running a single large application, Kubernetes distributes workloads across multiple small, efficient containers.
🔍 How is Kubernetes Different from Other Computing Services?#
Kubernetes is often compared to traditional virtual machines, Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) solutions, and serverless computing. Here’s how it stands out:
1️⃣ Kubernetes vs. Virtual Machines (VMs)#
Feature |
Kubernetes (Containers) |
Virtual Machines (VMs) |
|---|---|---|
Speed |
Fast startup & shutdown |
Slow boot times |
Resource Efficiency |
Shares OS kernel, lightweight |
Requires full OS per VM, heavy |
Scaling |
Automatic scaling of microservices |
Manual or pre-defined scaling |
Portability |
Runs anywhere with Kubernetes |
VM images tied to specific cloud providers |
Why Choose Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is far more efficient than VMs since containers share the same OS kernel.
It allows applications to start quickly, scale dynamically, and use fewer resources.
2️⃣ Kubernetes vs. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) (e.g., Heroku, Google App Engine)#
Feature |
Kubernetes |
PaaS (e.g., Heroku) |
|---|---|---|
Customization |
Fully customizable |
Limited customization |
Application Types |
Runs anything (stateful & stateless) |
Best for web apps |
Cloud Provider Lock-in |
Runs anywhere |
Often tied to a single provider |
Scaling |
Auto-scaling, fine-tuned control |
Auto-scaling but with predefined limits |
Why Choose Kubernetes?
Kubernetes provides more flexibility and can run any type of workload, including databases, AI models, and analytics pipelines.
PaaS services are easier for beginners but may restrict custom configurations.
3️⃣ Kubernetes vs. Serverless Computing (e.g., AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions)#
Feature |
Kubernetes |
Serverless (Functions-as-a-Service) |
|---|---|---|
Control |
Full control over workloads |
Abstracted infrastructure |
Long-Running Services |
Supports long-running apps |
Best for short-lived tasks |
Cost Efficiency |
Requires always-on resources |
Pay-per-use billing |
Performance |
No cold starts |
Can have cold start delays |
Why Choose Kubernetes?
More control: Kubernetes allows you to manage persistent applications like databases, AI models, and background workers.
Serverless is great for event-driven tasks, but Kubernetes supports long-running workloads with full visibility.
🌍 Where is Kubernetes Used in the Real World?#
🚢 Multi-Service Applications#
Companies like Spotify and Uber use Kubernetes to manage thousands of interconnected services.
📊 Data Processing & AI#
AI companies use Kubernetes to train machine learning models on massive datasets.
🎮 Gaming & Streaming#
Online gaming platforms ensure seamless multiplayer experiences across the globe.
🏦 Financial Services#
Banks use Kubernetes to handle millions of transactions securely every day.
📌 Key Takeaways#
✅ Composable deployments allow applications to be scalable, flexible, and resilient.
✅ Networking and storage make cloud applications accessible and reliable.
✅ Continuous rollouts enable faster, safer updates.
✅ Kubernetes offers more control than traditional VMs, PaaS, and serverless options.
✅ Containers provide lightweight, efficient, and portable application environments.
✅ Industries worldwide rely on Kubernetes to power critical applications.
🚀 The cloud is transforming how software is built—Kubernetes is at the heart of that change!

